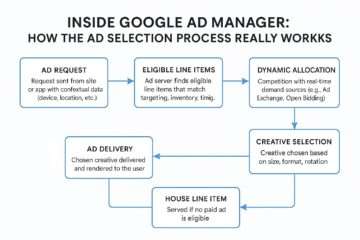

A federal US court found Google guilty of maintaining an unlawful monopoly over the online search and advertising markets in a historic ruling . We examine the ramifications of the decision, which represents a substantial victory for the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) and numerous state attorneys general.
The lawsuit, which was initially submitted in 2020, accused Google of utilizing its dominant position to stifle competition and preserve its monopoly in the search engine market.
The Department of Justice contended that Google’s actions are in violation of Section 2 of the Sherman Act, which prohibits monopolistic conduct. The matter was centered on Google’s exclusive agreements with companies like Apple, Samsung, and Verizon, which guaranteed that Google would remain the default search engine on their devices, thereby excluding competitors.
The 277-page ruling by Judge Amit Mehta was unambiguous in its condemnation of Google’s practices. He declared that Google “is a monopolist, and it has acted as such to preserve its monopoly.” The judge underscored that Google controls approximately 90% of the internet search market, with this percentage increasing to nearly 95% on mobile platforms. The ruling concluded that Google’s dominance was not solely attributable to the superiority of its search engine, but rather was substantially enhanced by anti-competitive practices.
Consequences for Google
The decision has significant implications for Alphabet Inc., the parent company of Google. The company may be compelled to modify its business practices and incur substantial penalties. This may involve restructuring portions of its operations or altering its approach to contract negotiations with other organizations. Nevertheless, Google has released a statement indicating that it intends to appeal the decision. According to Google, the public’s preference for the Google search engine is primarily due to its prevalence and user-friendliness, rather than its anti-competitive behavior.
As this case has the potential to establish a precedent for future antitrust actions against other tech companies, including Apple, Facebook, and Amazon, the tech industry has been closely monitoring it. Several industry professionals are of the opinion that this ruling could result in heightened scrutiny of other dominant actors in the technology sector.
The broader implications for the market and consumers
For consumers, the ruling has the potential to result in increased search engine options and potentially reduced prices for online advertising. Nevertheless, there are apprehensions that modifications to Google’s business model could potentially disrupt the services that millions of individuals depend on on a daily basis. This decision also brings into doubt the future of digital marketing, which is currently dominated by Google.
The legal dispute is far from concluded. The eventual outcome of Google’s appeal process is uncertain, and it could take years.
Nevertheless, this decision serves as a clear indication that regulators are committed to limiting the influence of Big Tech. It also emphasizes the significance of preserving competitive markets in the digital era.
The case against Google is a critical juncture in the ongoing endeavor to strike a balance between innovation and equitable competition. The ruling’s long-term implications could redefine the way we interact with digital services and reshape the tech industry, despite the fact that its immediate effects are still unfolding.